
If you have the forethought to become a part of the world of Python programming, the fundamental knowledge you should have is how to run a Python script. A Python script is a simple text file that contains a set of Python codes.
The standard method for writing a Python program is to use plain text editors. You can create Python scripts using any text editor you like.
- Before looking at the series of methods, the foremost step you should do is create the script file. For that, open your preferred text editor and write the code.
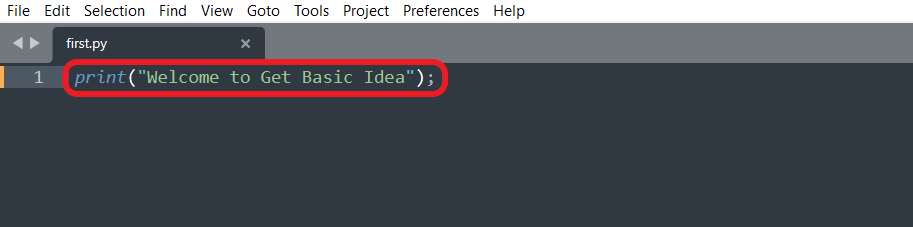
- Then save the file in your working directory as first.py. You can give any descriptive name to your script file. But keep in mind, you need to provide the .py extension.
Method 1: Run a Python script using Command-Line
[g_article_ads]
The command line is known as Command Prompt on Windows. You can access this by clicking the start menu and search for command prompt or cmd.
There are few ways to run the script using the command prompt. Let us see them one by one.
1. Using the Python Command
The simplest way to execute a Python script is to use the Python command.
- First, go to your Command Prompt and type python or python 3 (depending on your Python version), followed by the script file path.

- Then hit Enter. You will see the output on your screen.

- If you do not receive the output, you should verify your system path and file location. If it still does not work, then reinstall the Python software on your computer and try again.
2. Redirecting the output
Redirecting means saving the output of the script file to another file. Instead of using standard system output, it may be helpful for later analysis. This process is called stream redirection.
- To do this method, go to the command prompt and type your code like this.

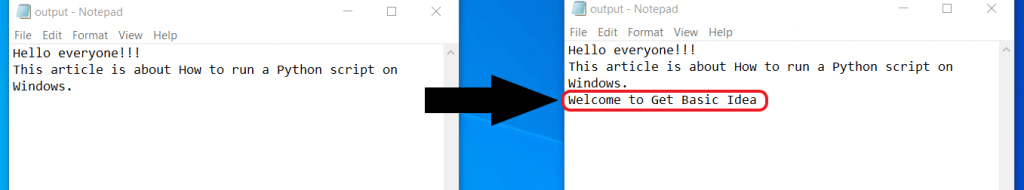
- This method redirects the output to the output.txt file.
Do you know what happens when you redirect the output of the Python script to another file?
[g_article_ads]
There are two types of scenarios that can be possible when redirecting the output.
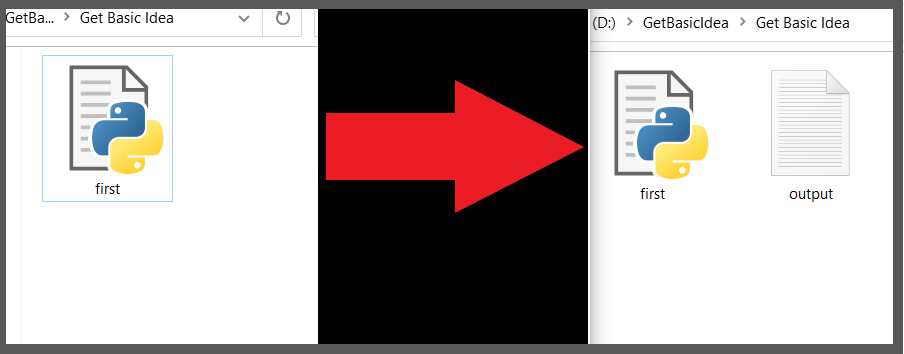
1. The output.txt file does not exist in your working directory.
- In this scenario, the system will automatically create the new file and save the output in it.
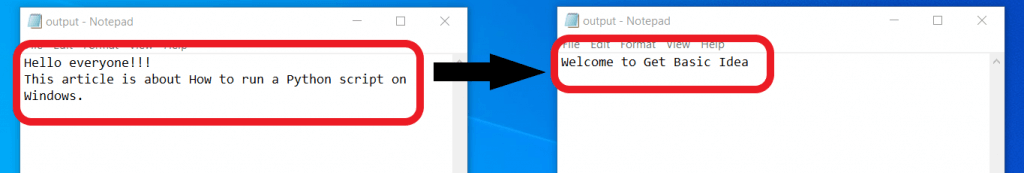
2. The output.txt file already exists in your working directory.
- The system will automatically detect the file and replace the contents available in the existing file with the new output.
- If you want to insert the output of continuous executions at the end of the file instead of replacing it, you should type in two angle brackets (>>) rather than one. By doing this, the system will append the output at the end of the existing file.
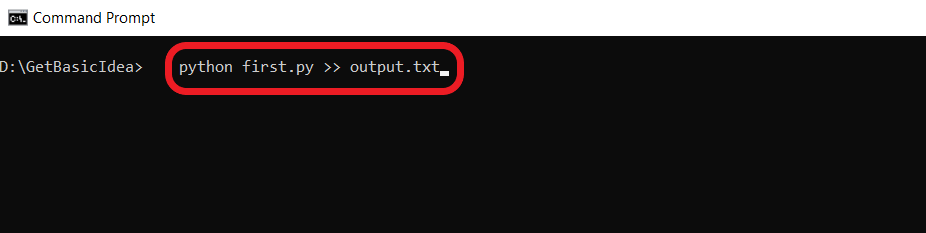
- The output will be like this.
3. Running modules with -m option
[g_article_ads]
- To use this method, go to the command prompt and type like this.
python -m <Module Name>

- It explores the module name in the system path and runs the content.
- The module name should be the name of a module object, not a string.
4. Using the script filename
- In this method, you only need to enter the script file name on the command prompt.

This method is only possible on the latest versions of Windows because it handles the system registers and file association to establish the program that must run a specific file.
Though, if it does not work, you might need to verify the script location whether it is available in the current working directory or not.
Method 2: Run a Python script interactively
[g_article_ads]
Open the command prompt, type python or python3, and press Enter to start a Python interactive session.
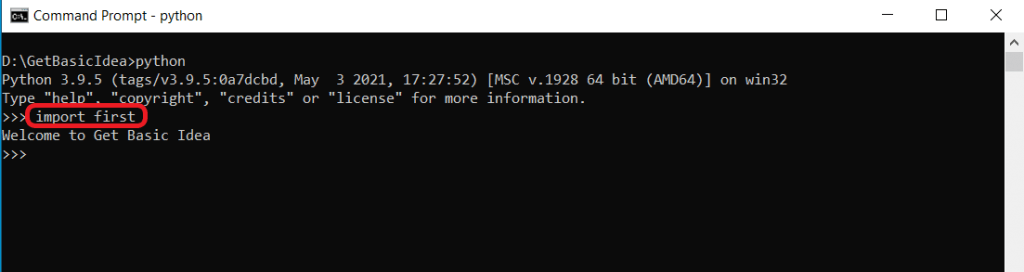
1. Using import module
What happens when you use the import module is that you load the module with its contents. This option only works once per session. Even if you change the module content after the first import, your continuous import processes will not do anything.
2. Using importlib module
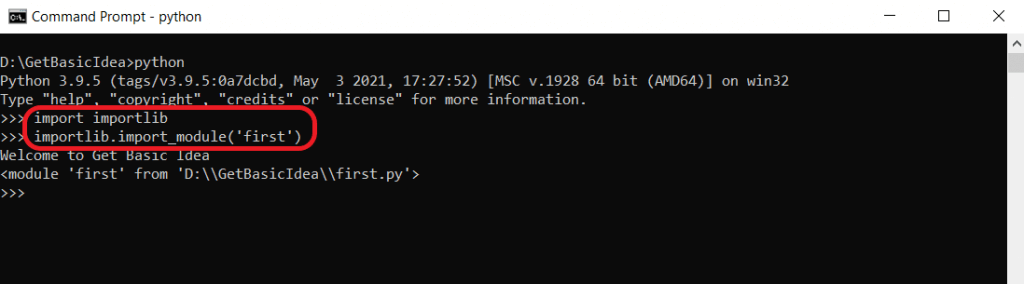
importlib is the implementation of the import module. This module is available in the Python Standard Library. This module provides the import_module() function. With the help of this function, you can follow an import process and then run any script or module.
Once you have imported a module for the first time, you will not be able to use the import method again. In this scenario, you can use importlib.reload(), which forces the interpreter to re-import the module.
The argument of reload() should be the name of a module object, not a string.
3. Using exec()
[g_article_ads]
So far, you have seen the generally used ways to run Python scripts. In this section, you will find another possible way to execute your scripts using exec(). It is a built-in function that supports the dynamic execution of the Python code.
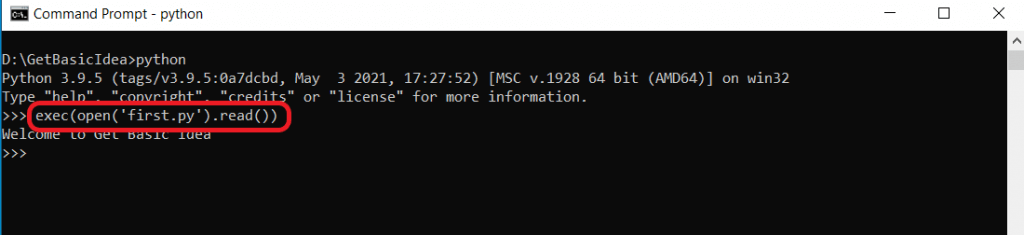
This line of code opens the first.py script file, reads its contents, and sends it to exec() function, which finally executes the code.
- Note: To exit from the interactive mode, type 'exit()' and then press 'Enter' or press 'Ctrl + Z' and press 'Enter'.
Method 3: Run a Python script from an IDE or Text editor
When creating complex applications, the recommended way of writing Python is using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) or an Advanced Text Editor.
1. Using an IDE
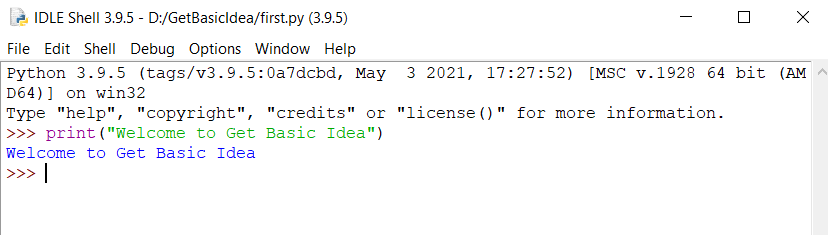
When you install Python, the IDLE is installed by default. IDLE is a conventional IDE for learning.
- Open the IDLE, create a new file and save the script file with the .py extension. Then write the code and click Enter.
2. Using a Text Editor
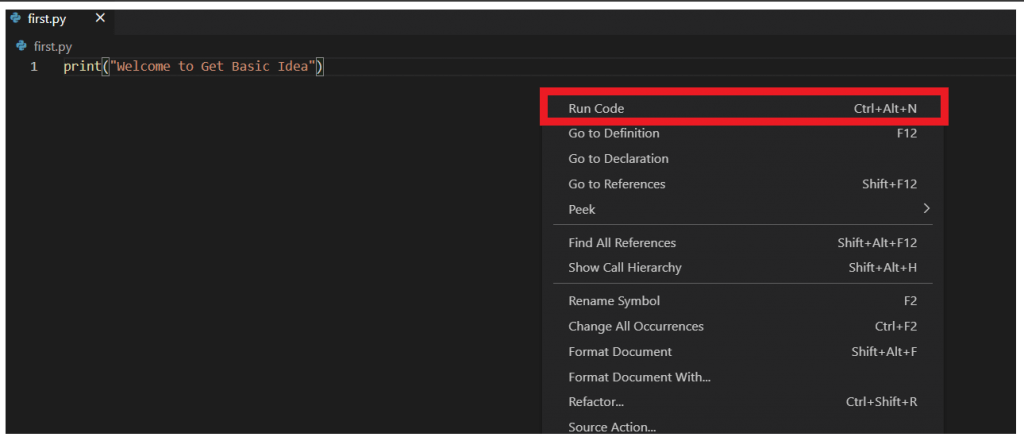
- Open your text editor and write the piece of code and save the file with the .py extension. Then right-click anywhere in the text area and select the option 'Run Code'.
Method 4: Run a Python script from a file manager
[g_article_ads]
You can run the script by double-clicking its icon in the file manager. To use this method, you need to save the file with the extension .py for python.exe.
- When you double-click on the script, you will only see a flash of a black window on your screen. To avoid this scenario, add the statement "input('Enter')" at the end of the script file. It exits the program only when you press Enter.
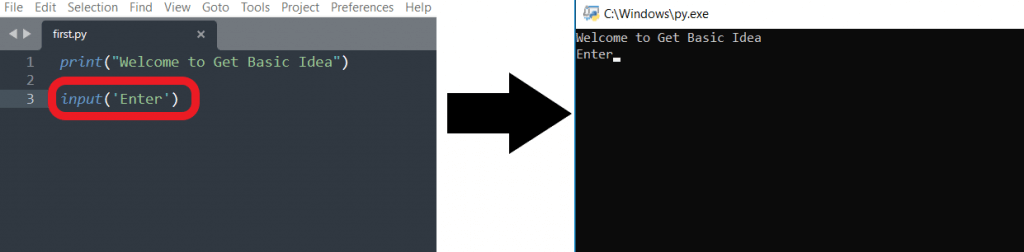
- If there is an error in your script, the execution will stop before the input() statement is reached, and you will not be able to see the result.
I hope you all have understood how to run a Python script on Windows. I'll meet you all soon with more exciting content.
Author of Get Basic Idea / Undergraduate at University of Moratuwa.
