All You Need to Know About Digital Twin
A Digital Twin is a digitally created representation of a physical object, environment, process, or service. Digital twin technology can be used to run simulations to gather data and forecast how they will function.
In brief, a digital twin is a virtual representation created to accurately represent a physical phenomenon. The object being researched is equipped with a variety of sensors relevant to critical areas of functionality. These sensors generate data on various aspects of the physical object's operation, including energy output, temperature, weather conditions, and so on. This information is then sent to a processing machine and integrated into the digital version of the object.
Once provided with such information, the virtual model may be used to run simulations, investigate performance concerns, and produce potential changes, all to create valuable insights that can later be applied to the real physical device.
History of Digital Twin
David Gelernter's book Mirror Worlds, published in 1991, introduced the concept of digital twin technology. However, Dr. Michael Grieves is credited with first bringing the notion of digital twins to the industry in 2002 and formally presenting the digital twin software idea.

In 2002, NASA began using digital twin technology for space exploration missions. They created virtual models of spacecraft and systems to monitor and troubleshoot issues remotely during missions.
Over time, the application of digital twins expanded beyond manufacturing to various industries such as healthcare, automotive, smart cities, and infrastructure. This expansion was fueled by advancements in IoT, data analytics, and simulation technologies. Digital twin technology became closely associated with the Industry 4.0 paradigm, which emphasizes the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing and other industries. Digital twins were seen as a key enabler for achieving smart, connected, and autonomous systems.
As computing power increased and the cost of sensors and data storage decreased, digital twin technology matured and became more accessible to a wider range of industries. Companies began to invest in digital twin initiatives to improve product design, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques with digital twin technology has further enhanced its capabilities. AI-powered digital twins can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, predict future behavior, and autonomously optimize system performance.
How does the Digital Twin work?
A Digital Twin has three main elements. The first one is a Physical Entity or the original version of the system. The next one is the Software form of the entity which is the Digital Twin. And the next part is the link between these two elements.
The developers who design digital twins make sure the virtual computer representation can get feedback from sensors that collect data from the real-world counterpart. This enables the digital version to replicate and recreate everything that happens with the initial version in real-time, providing the opportunity to gain insights about the performance and potential problems.
Digital Twin Types
The classification of Digital Twin can be different from their purpose. Most commonly they are classified under four types.
- Component Twins (Part Twins)
- Asset Twins (Product Twins)
- System Twins (Unit Twins)
- Process Twins
However, there are several types of Digital Twins based on their applications and functionalities.
- Product Twins
- Process Twins
- System Twins
- Healthcare Twins
- City Twins
- Building Twins
- Human Twins
- Supply Chain Twins
Product Twins
These digital twins replicate physical products or assets, such as machinery, vehicles, or consumer goods. Product twins can be used for design optimization, predictive maintenance, and performance monitoring.
Process Twins
Process twins simulate manufacturing processes, supply chain operations, or other industrial processes. The macro level of magnification shows how systems collaborate to produce an entire manufacturing facility. Are all of those systems synchronized so that they run at peak efficiency, or will disruptions in one influence the others? Process twins can aid in the development of precise timing systems, which in turn influence overall efficacy. These twins help optimize production efficiency, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall process performance.
System Twins
System twins replicate complex systems such as power grids, transportation networks, or smart cities. They enable better management, optimization, and decision-making within these systems. They also allow you to observe several assets work together to build a fully functional system. System twins provide insight into asset interactions and can recommend performance improvements.
Healthcare Twins
Healthcare twins model individual patients or healthcare facilities to support personalized treatment plans, optimize resource allocation, and improve patient outcomes.
City Twins
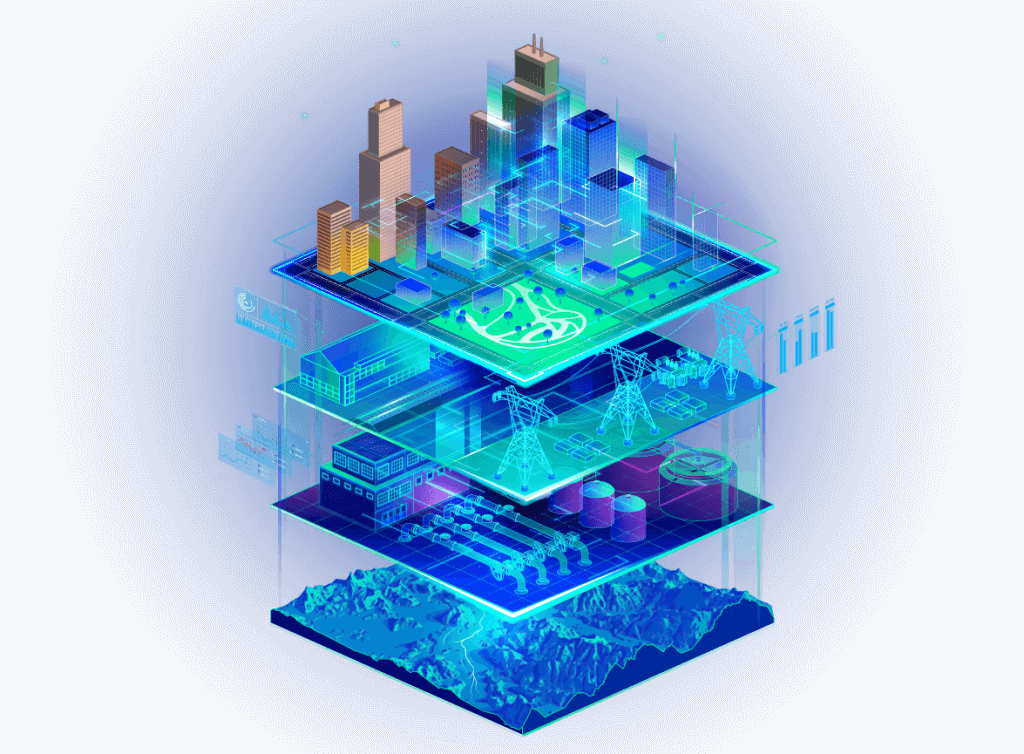
City twins simulate entire urban environments, including infrastructure, transportation systems, and public services. They help urban planners make informed decisions about city development, sustainability, and resilience.
Building Twins
Building twins represent individual buildings or complexes for facilities management, energy optimization, and space utilization.
Human Twins
Human twins model individual humans, often for healthcare, wellness, or performance optimization purposes. They can integrate data from wearable devices, medical records, and genetic information to provide personalized insights.
Supply Chain Twins
Supply chain twins simulate the end-to-end supply chain processes, including sourcing, production, logistics, and distribution. They help optimize inventory levels, reduce lead times, and improve supply chain resilience.
How does Digital Twin impact the industry?
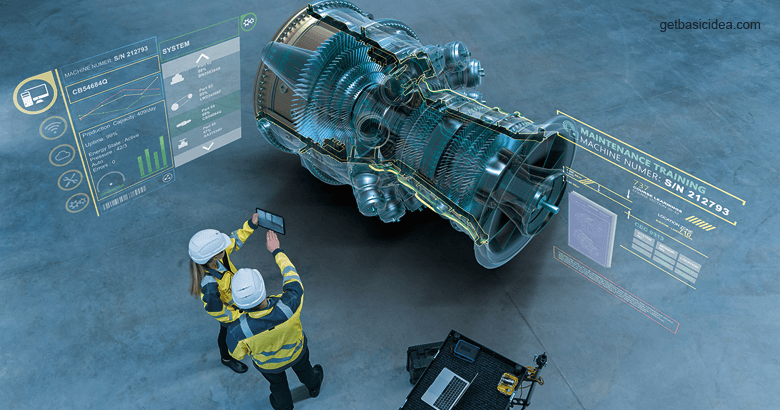
Let's inquire what types of advantages Digital Twin can bring to organizations and industries.
- Reduce marketing time
- Enable quick iterations and optimizations of product designs
- Significant improvement in product quality
- Simulating the product throughout the production process allows for the early detection of design problems
- Longer equipment up-time due to maintenance issues can be evaluated in a single digital twin rather than shutting down the entire system to isolate a problem
- Improved product end-of-life procedures, such as refurbishing and recycling, as a result of more precise product age and content information
- Help organizations reduce the material utilized in a product's design
- Improve product traceability to minimize environmental waste
Industries that use Digital Twin technology
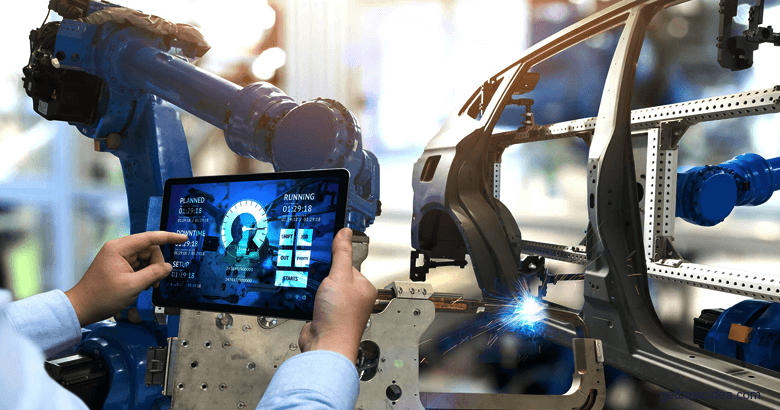
McKinsey has seen organizations raise sales by up to 10% by creating digital twins of their consumers, allowing them to completely participate and immerse themselves in the company's product.
Daimler has created customer twins that allow consumers to test drive a vehicle without really getting behind the wheel.
Consumer electronics makers have significantly improved sustainability by adopting digital twins, cutting scrap waste by approximately 20%.
Visit the previous post about Neuralink's brain chip has Got the approval for human study.
Author of Get Basic Idea – The Knowledge Base / Bachelor of Technology – BTech, Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering.



