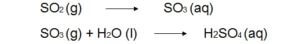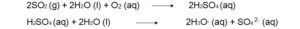Acid Rain | Environmental Chemistry
What is an acid rain?
Acid rain is a rain with a lower pH value than the normal natural rain. It has a lower pH value which lies between pH 4 to pH 5. Sometimes the pH value can be lower than pH 4. Usually, the natural rain water is slightly acidic. Its pH value is about pH 5.1-pH 5.8. It is due to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) as a result of the solvation of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) in the rain water. The partial ionization of carbonic acid is responsible for the slight acidity of natural rain water. Solvation of acidic gases other than CO2 in rain water causes an acid rain. The oxides of sulphur (SOx) and nitrogen (NOx) are the major contributors for the formation of acid rains.
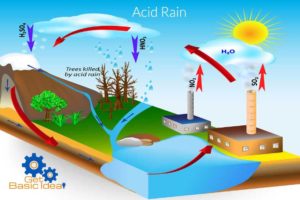
The formation of an acid rain.
The salvation of acidic gases present in the atmosphere is caused to acidify the water. The acidity depends on;
- Solubility of the gas in water
- Strength of the acid formed by the gas
Even though the percentage of CO2 is higher in the atmosphere it does not contribute for the formation of acid rain due to its low acidity. But the presence of highly acidic gaseous oxides like SOx, NOx, even in very small amount can acidify water in a higher extent. SO2 and NO2 gases are considered as the major contributors for this incident. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide can form sulfuric and nitric acid respectively by solving in the water increasing its acidity.
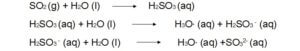
Reactions of atmospheric sulfur dioxide (SO2).
1.
2. Oxidants such as Oxygen (O2), atomic oxygen (O), hydroxyl free radicals (OH) can convert SO2 into SO3.This sulphur trioxide (SO3) can easily converted into sulphuric acid by dissolving in water.
3. SO2 and oxidant both can dissolve in a single water droplet and can form sulphuric acid. Water act as the reaction medium and facilitates the oxidation process.
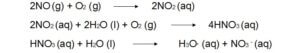
Reactions of atmospheric nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Factors affect for the formation of acid rain.
Main reason is the air pollution made by the mankind. Some natural incidents can also cause the acid rain.
- Emissions of power plants.
- Exhausted fumes of motor vehicles.
- Burning of fossil fuels such as petrol, diesel and coal.
- Industrial processes that emit oxides of sulfur and nitrogen.
- Lightening.
- Volcanic eruptions.
Environmental effects caused by acid rain.
- Harmful to vegetation and adverse effects on sensitive ecosystems.
- Acidity of soil is increased and lead to decrease the quality of soil. It can cause reduce the diversity of microorganisms.
- Depletion of aquatic species due to increased acidity in natural water resources (lakes. Rivers).
- Causes irreparable damages to buildings and statues especially those made out of marble.
- Can cause damages to power plants.
- Depletion of natural corals.
- Adverse effects on agriculture.
Admin of Get Basic Idea / Senior Solution Architect.