Learn about Blockchain – Basics (Part 1)
Blockchain is the future.
What, when, why, and how? Those were the types of questions popping into my mind when I first heard about blockchain. Fascinated by what it does and what it holds the possibility of doing in the future, I wanted to learn more.
Reading about it and still much more to explore made me realize how important it was to get a basic understanding of it.
I wrote this to help beginners learn about blockchain better. Here is an attempt at breaking down what it is.
Early History: Who created blockchain?
Year – 1991
Co-inventors: Scientists Stuart Haber (Ph.D. in computer science from Colombia University) and Scott Stornetta (Ph.D. in physics from Stanford University)
To solve the problem of the immutability of digital records, Haber and Stornetta introduced blockchain technology.
They wanted a solution where no one could tamper with the timestamps of digital documents while also maintaining the document’s integrity. So they both developed a system with the use of cryptography.
What is blockchain?
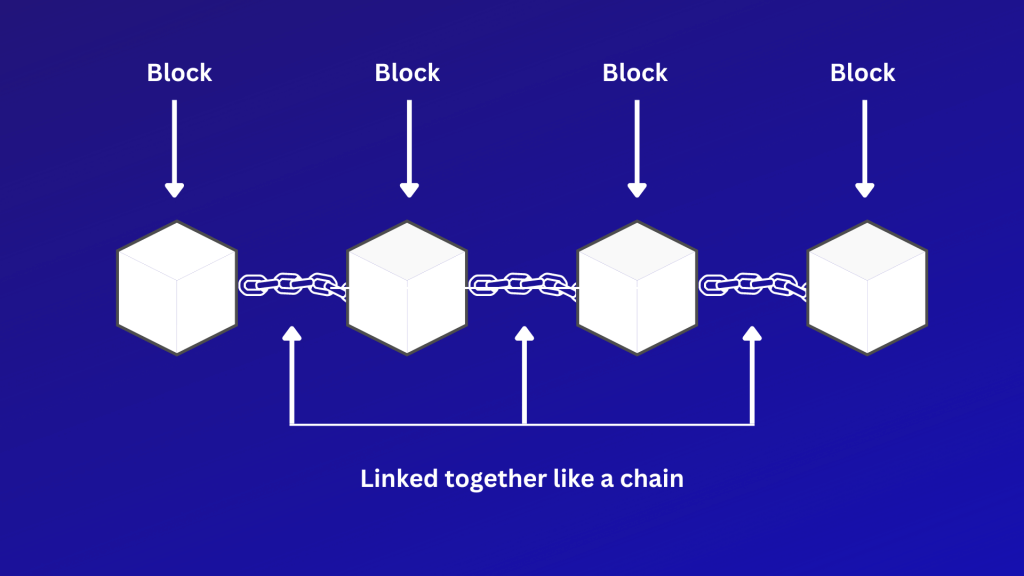
A blockchain is a distributed digital record of data. It is a way of storing information in chronological order.
The data is stored in blocks, and each block of data is permanently linked one after the other forming a chain that is;
- Immutable – permanent, cannot be hacked or altered
- Decentralized – no central governing authority
- Distributed – shared and synchronized across a network
What type of data does a block hold?
In a blockchain database, a block is where the data (information) is stored.
These consists of
- monetary transactions
- digital information
- medical records
- contracts
- assets and more
What are the features of blockchain?
Immutable, distributed, and decentralized are the key areas that make blockchain what it is and it also includes other features listed below.
- Enhanced Security – Records in the blockchain are encrypted using cryptography
- Consensus mechanism – Consensus algorithms help the network make quick and unbiased decisions by agreeing (kind of like a voting system)
- Faster settlement – A much quicker way of processing transactions
- Transparency – It's a distributed ledger therefore information is available to everyone
- Cannot be corrupted – It's immutable and every node on the network has a copy so only valid information gets added
I will further dive deep into each feature in the coming blogs.
Advantages & Drawbacks of blockchain
Blockchain technology has risen in popularity ever since Bitcoin was introduced. We see it being talked about and used more than ever before. Hopefully, a revolutionary change is not too far.
Advantages
- It offers true traceability. Making it easy to track errors
- Protects business processes with its high level of security
- There is no single-point-of-failure
- A reliable trustless system
- Makes use of smart contracts
- Eliminates the middleman thus reducing costs (no third parties)
- Everyone can verify the correctness of the information
Drawbacks
- Requires more storage space
- Regulations from some financial institutions
- High implementation costs
- Scalability issues
- Data is immutable
- High energy consumption for some
Use cases of blockchain technology
Though most commonly used and known, blockchain is not limited to cryptocurrencies only. It can be used in various other industry sectors as well such as:
- Supply Chain & Logistics
- Healthcare
- Retail & eCommerce
- Finance
- Property & Real Estate
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Insurance
- Travel and Transportation
- Music
Stay tuned for Part 2 of our "Learn About Blockchain" series.
Author of Get Basic Idea – Knowledge Base.



